FabulousFusionFood's Bermudan Recipes Home Page
 The flag of Bermuda (left) and the coat of arms of Bermuda (right).
The flag of Bermuda (left) and the coat of arms of Bermuda (right).
Welcome to the summary page for FabulousFusionFood's Bermudan recipes, part of the Caribbean. This page provides links to all the Bermudan recipes presented on this site, with 22 recipes in total.
This is a continuation of an entire series of pages that will, I hope, allow my visitors to better navigate this site. As well as displaying recipes by name, country and region of origin I am now planning a whole series of pages where recipes can be located by meal type and main ingredient. This page gives a listing of all the Indian recipes added to this site.
Bermuda is a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean The capital is Hamilton and the largest city is St George's. Bermuda is an archipelago consisting of 181 islands, although the most significant islands are connected by bridges and appear to form one landmass. It has a land area of 54 square kilometres.
Bermudan cuisine blends British and Portuguese cuisine with preparations of local seafood species, particularly wahoo and rockfish. Traditional dishes include codfish and potatoes served either with an add-on of hard-boiled egg and butter or olive oil sauce with a banana or in the Portuguese style with tomato-onion sauce, peas and rice. Hoppin' John, pawpaw casserole and fish chowder are also specialties of Bermuda.
Bermuda historically known as the Bermudas or Somers Isles) is a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, about 1,035 km (643 mi) to the west-northwest.
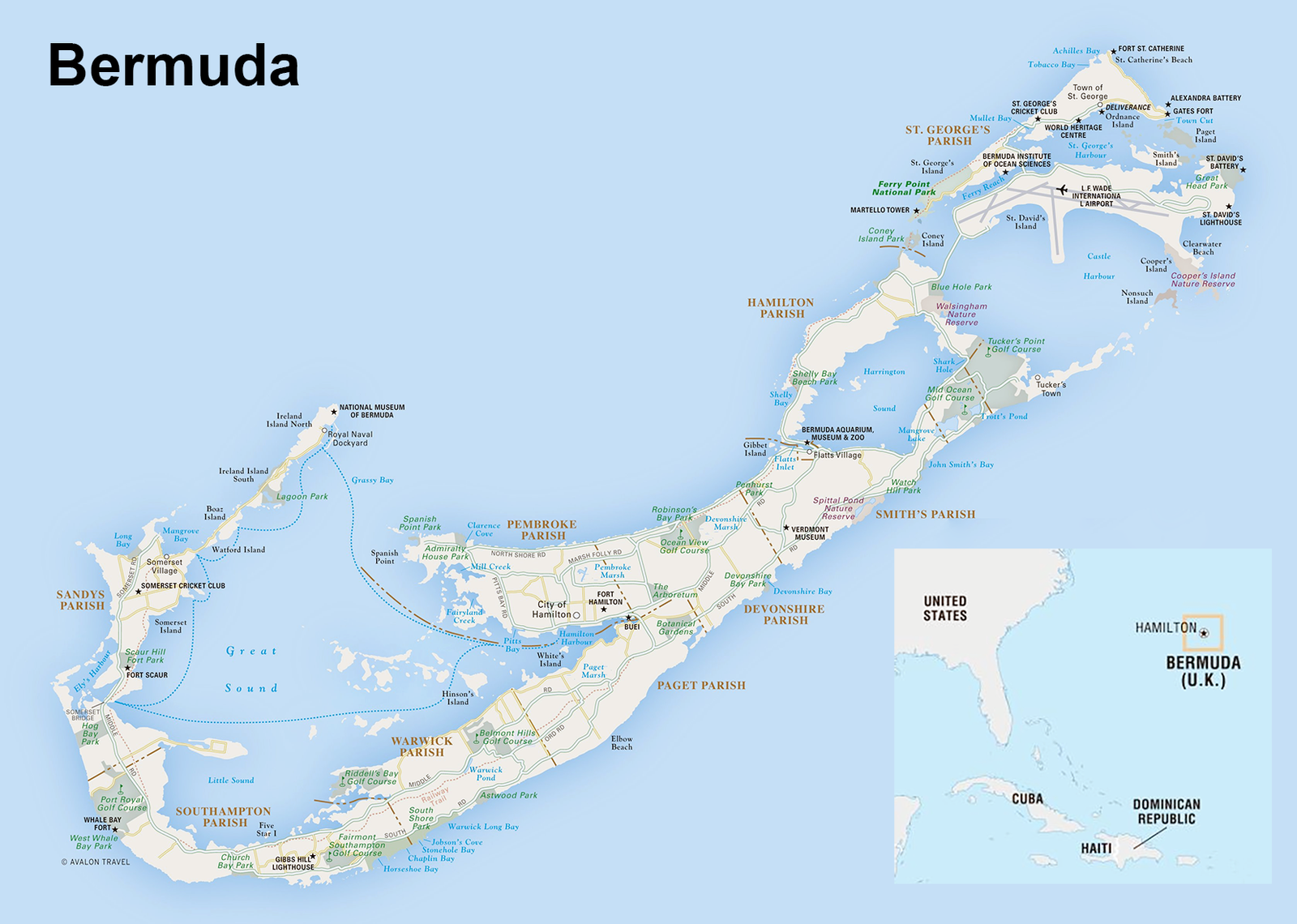 Image of the Bermudan archipelago with the location of Bermuda in relation
Image of the Bermudan archipelago with the location of Bermuda in relation
to the Caribbean and Eastern US shown, inset.Bermuda is an archipelago consisting of 181 islands, although the most significant islands are connected by bridges and appear to form one landmass. It has a land area of 54 square kilometres. Bermuda has a tropical climate, with warm winters and hot summers. Its climate also exhibits oceanic features similar to other coastal areas in the Northern Hemisphere with warm, moist air from the ocean ensuring relatively high humidity and stabilising temperatures. Bermuda is prone to severe weather from recurving tropical cyclones; however, it receives some protection from a coral reef and its position north of the Main Development Region, which limits the direction and severity of approaching storms.
Bermuda is named after Spanish explorer Juan de Bermúdez, who discovered the archipelago in 1505. The islands have been permanently inhabited since 1612 when an English settlement was established at St. George's, which is also the territory's largest settlement. Forming part of British America, Bermuda was governed under Royal charter by the Somers Isles Company until 1684, when it became a crown colony. The first enslaved Africans were taken to Bermuda in 1616. The Somers Isles Company ensured a steady flow of free but indentured servants until 1684, and most tobacco farms owned by overseas adventurers were sold to the tenants or other occupants after Bermuda-grown tobacco became steadily less profitable following the 1620s, becoming family farms that switched from growing tobacco for export to producing food (initially for local consumption). Consequently, a plantation economy did not develop and the slave trade largely ceased by the end of the 17th century. The economy instead became maritime-focused, with the colony serving as a base for merchants, privateers and the Royal Navy, giving its name to the Bermuda rig and Bermuda sloop. It became an imperial fortress, the most important British naval and military base in the western hemisphere with vast funds lavished on its Royal Naval Dockyard and military defences until the 1950s. Tourism has been a significant contributor to Bermuda's economy since the 19th century and after World War II, the territory became a prominent offshore financial centre and tax haven.
Divided into nine parishes, Bermuda is a self-governing parliamentary democracy with a bicameral parliament located in the capital Hamilton. The House of Assembly dates from 1620, making it one of the world's oldest legislatures. The premier is the head of government and is formally appointed by the governor, who is nominated by the British government as the representative of the King. The United Kingdom is responsible for foreign affairs and defence. An independence referendum was held in 1995 with a large majority voting against independence. As of 2019, Bermuda had a population of around 64,000 people, making it the second-most populous of the British Overseas Territories. Black Bermudians, a diverse population primarily of any mixture of African, European, and Native American ancestry, make up around 50% of the population, while White Bermudians, primarily of British, Irish and Portuguese descent, make up 30% of the population. There are smaller groups from other races or identifying as mixed race and about 30% of the population is not Bermudian by birth. The last remaining colony in the former British North America (following the 1867 Confederation of Canada and the Colony of Newfoundland becoming the Dominion of Newfoundland in 1907), Bermuda has a distinct dialect of English and has historically had strong ties with other English-speaking countries in the Americas, including the United States, Canada, and the Commonwealth Caribbean. It is an associate member of the Caribbean Community.
Etymology: Bermuda is named after the Spanish sailor Juan de Bermúdez, who discovered the islands in 1505, while sailing for Spain from a provisioning voyage to Hispaniola in the ship La Garça.
There are several dishes served on Bermuda that are unique to the island which offer a taste of traditional Bermudian culture. Fish is one of the main ingredients in Bermudian cuisine. Local fish includes mahi mahi/dolphinfish, snapper, spiny lobster (during September–March), tuna, and wahoo. These are used in dishes such as fish and chips, panfried fish, and boiled salted codfish and potato, a traditional dish in Bermuda (usually served on Sundays with tomato sauce and olive oil).
Bermuda fish chowder is considered a national dish, which is a staple food not only in restaurants and hotels but also in homes; the main ingredients are fish stock, fish, vegetables and bacon fat. It is served with spices, as well as black rum and sherry peppers. Beef stock is an essential ingredient in Bermudian fish chowder.
This is a continuation of an entire series of pages that will, I hope, allow my visitors to better navigate this site. As well as displaying recipes by name, country and region of origin I am now planning a whole series of pages where recipes can be located by meal type and main ingredient. This page gives a listing of all the Indian recipes added to this site.
Bermuda is a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean The capital is Hamilton and the largest city is St George's. Bermuda is an archipelago consisting of 181 islands, although the most significant islands are connected by bridges and appear to form one landmass. It has a land area of 54 square kilometres.
Bermudan cuisine blends British and Portuguese cuisine with preparations of local seafood species, particularly wahoo and rockfish. Traditional dishes include codfish and potatoes served either with an add-on of hard-boiled egg and butter or olive oil sauce with a banana or in the Portuguese style with tomato-onion sauce, peas and rice. Hoppin' John, pawpaw casserole and fish chowder are also specialties of Bermuda.
Bermuda historically known as the Bermudas or Somers Isles) is a British Overseas Territory in the North Atlantic Ocean. The closest land outside the territory is in the American state of North Carolina, about 1,035 km (643 mi) to the west-northwest.
 Image of the Bermudan archipelago with the location of Bermuda in relation
Image of the Bermudan archipelago with the location of Bermuda in relationto the Caribbean and Eastern US shown, inset.
Bermuda is named after Spanish explorer Juan de Bermúdez, who discovered the archipelago in 1505. The islands have been permanently inhabited since 1612 when an English settlement was established at St. George's, which is also the territory's largest settlement. Forming part of British America, Bermuda was governed under Royal charter by the Somers Isles Company until 1684, when it became a crown colony. The first enslaved Africans were taken to Bermuda in 1616. The Somers Isles Company ensured a steady flow of free but indentured servants until 1684, and most tobacco farms owned by overseas adventurers were sold to the tenants or other occupants after Bermuda-grown tobacco became steadily less profitable following the 1620s, becoming family farms that switched from growing tobacco for export to producing food (initially for local consumption). Consequently, a plantation economy did not develop and the slave trade largely ceased by the end of the 17th century. The economy instead became maritime-focused, with the colony serving as a base for merchants, privateers and the Royal Navy, giving its name to the Bermuda rig and Bermuda sloop. It became an imperial fortress, the most important British naval and military base in the western hemisphere with vast funds lavished on its Royal Naval Dockyard and military defences until the 1950s. Tourism has been a significant contributor to Bermuda's economy since the 19th century and after World War II, the territory became a prominent offshore financial centre and tax haven.
Divided into nine parishes, Bermuda is a self-governing parliamentary democracy with a bicameral parliament located in the capital Hamilton. The House of Assembly dates from 1620, making it one of the world's oldest legislatures. The premier is the head of government and is formally appointed by the governor, who is nominated by the British government as the representative of the King. The United Kingdom is responsible for foreign affairs and defence. An independence referendum was held in 1995 with a large majority voting against independence. As of 2019, Bermuda had a population of around 64,000 people, making it the second-most populous of the British Overseas Territories. Black Bermudians, a diverse population primarily of any mixture of African, European, and Native American ancestry, make up around 50% of the population, while White Bermudians, primarily of British, Irish and Portuguese descent, make up 30% of the population. There are smaller groups from other races or identifying as mixed race and about 30% of the population is not Bermudian by birth. The last remaining colony in the former British North America (following the 1867 Confederation of Canada and the Colony of Newfoundland becoming the Dominion of Newfoundland in 1907), Bermuda has a distinct dialect of English and has historically had strong ties with other English-speaking countries in the Americas, including the United States, Canada, and the Commonwealth Caribbean. It is an associate member of the Caribbean Community.
Etymology: Bermuda is named after the Spanish sailor Juan de Bermúdez, who discovered the islands in 1505, while sailing for Spain from a provisioning voyage to Hispaniola in the ship La Garça.
Barbadian/Bajan Cuisine:
Bermudian cuisine blends British and Portuguese cuisine with preparations of local seafood species, particularly wahoo and rockfish. Traditional dishes include codfish and potatoes served either with an add-on of hard-boiled egg and butter or olive oil sauce with a banana or in the Portuguese style with tomato-onion sauce, peas and rice. Hoppin' John, pawpaw casserole and fish chowder are also specialties of Bermuda. As most ingredients used in Bermuda's cuisine are imported, local dishes are offered with a global blend, with fish as the major ingredient, in any food eaten at any time.There are several dishes served on Bermuda that are unique to the island which offer a taste of traditional Bermudian culture. Fish is one of the main ingredients in Bermudian cuisine. Local fish includes mahi mahi/dolphinfish, snapper, spiny lobster (during September–March), tuna, and wahoo. These are used in dishes such as fish and chips, panfried fish, and boiled salted codfish and potato, a traditional dish in Bermuda (usually served on Sundays with tomato sauce and olive oil).
Bermuda fish chowder is considered a national dish, which is a staple food not only in restaurants and hotels but also in homes; the main ingredients are fish stock, fish, vegetables and bacon fat. It is served with spices, as well as black rum and sherry peppers. Beef stock is an essential ingredient in Bermudian fish chowder.
The alphabetical list of all the Bermudan recipes on this site follows, (limited to 100 recipes per page). There are 22 recipes in total:
Page 1 of 1
| Bermuda Chicken Origin: Bermuda | Bermuda Rockfish with Bananas and Rum Sauce Origin: Bermuda | Cassava Pie Origin: Bermuda |
| Bermuda Chicken Curry Origin: Bermuda | Bermuda Salmon Origin: Bermuda | Farina Pie Origin: Bermuda |
| Bermuda Curry Powder Origin: Bermuda | Bermudan Fishcakes Origin: Bermuda | Mussel Pie Origin: Bermuda |
| Bermuda Fish Chowder Origin: Bermuda | Bermudan Fried Fish Origin: Bermuda | Salt Cod and Potatoes Origin: Bermuda |
| Bermuda Fish Chowder II Origin: Bermuda | Bermudan Hot Cross Buns Origin: Bermuda | Sherry Pepper Sauce Origin: Bermuda |
| Bermuda Onion and Potato Salad Origin: Bermuda | Bermudan Plantain Curry Origin: Bermuda | Sweet Potato Casserole Origin: Bermuda |
| Bermuda Peas n' Rice Origin: Bermuda | Bermudan Potato Salad Origin: Bermuda | |
| Bermuda Rockfish Coconut Curry Origin: Bermuda | Bermudan Spinach Salad Origin: Bermuda |
Page 1 of 1