FabulousFusionFood's Barbadian/Bajan Recipes Home Page
 The flag of Barbados (left) and the coat of arms of Barbados (right).
The flag of Barbados (left) and the coat of arms of Barbados (right).
Welcome to the summary page for FabulousFusionFood's Barbadian/Bajan recipes, part of the Caribbean. This page provides links to all the Barbadian/Bajan recipes presented on this site, with 19 recipes in total.
This is a continuation of an entire series of pages that will, I hope, allow my visitors to better navigate this site. As well as displaying recipes by name, country and region of origin I am now planning a whole series of pages where recipes can be located by meal type and main ingredient. This page gives a listing of all the Indian recipes added to this site.
Barbadian/Bajan is an island country within the Lesser Antilles of the Atlantic Ocean. The capital is Bridgetown. The island is is 34 kilometres long and up to 23 km wide, covering an area of 439 km2.
Barbadian/Bajan cuisine is a mixture of African, Indian, Irish, Creole and British influences. A typical meal consists of a main dish of meat or fish, normally marinated with a mixture of herbs and spices, hot side dishes, and one or more salads.
Barbados is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles region of the West Indies. Despite not bordering the Caribbean Sea, it is considered to be part of the Caribbean region and is therefore the most easterly of the Caribbean islands. It lies on the boundary of the South American and Caribbean plates. Its capital and largest city is Bridgetown. It was colonized by the British and forms part of the Commonwealth.
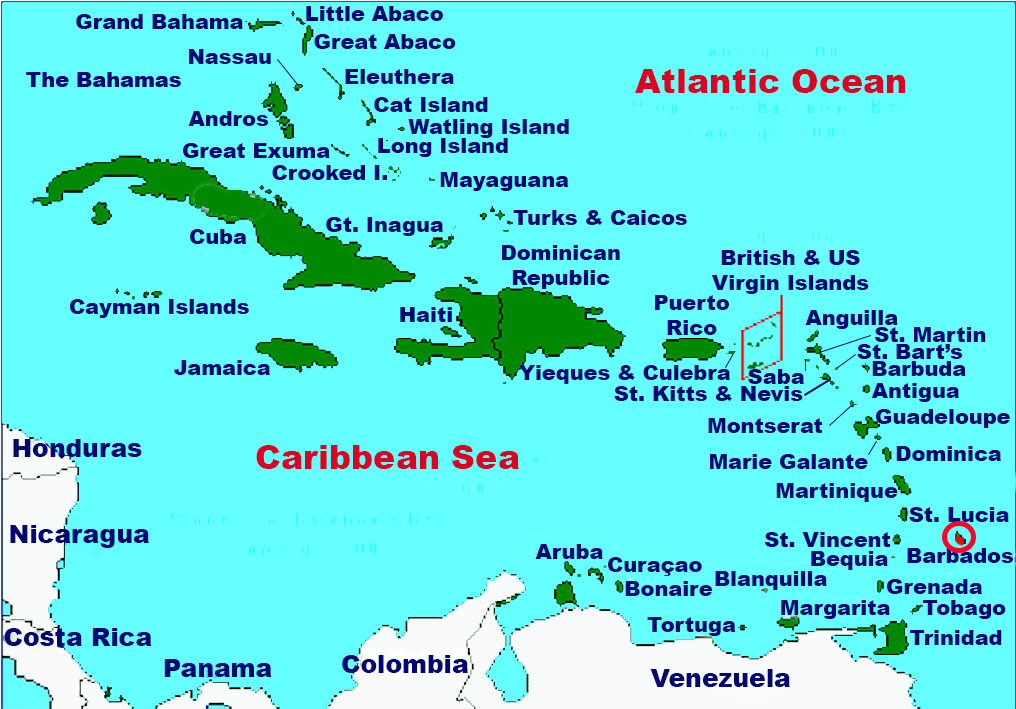 Location of Barbados in the Caribbean with the land mass of
Location of Barbados in the Caribbean with the land mass of
Barbados picked out and circled in red.Inhabited by Kalinago people since the 13th century, and prior to that by other Indigenous peoples, Barbados was claimed for the Crown of Castile by Spanish navigators in the late 15th century. It first appeared on a Spanish map in 1511. The Portuguese Empire claimed the island between 1532 and 1536, but abandoned it in 1620 with their only remnants being the introduction of wild boars to supply of meat whenever the island was visited. An English ship, the Olive Blossom, arrived in Barbados on 14 May 1625; its men took possession of the island in the name of King James I. In 1627, the first permanent settlers arrived from England, and Barbados became an English and later British colony. During this period, the colony operated on a plantation economy, relying on the labour of African slaves who worked on the island's plantations. Slavery continued until it was phased out through most of the British Empire by the Slavery Abolition Act 1833.
On 30 November 1966, Barbados moved toward political independence and assumed the status of a Commonwealth realm, becoming a separate jurisdiction with Elizabeth II as the Queen of Barbados. On 30 November 2021, Barbados transitioned to a republic within the Commonwealth, replacing its monarchy with a ceremonial president.
The country gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1973, led by Sir Lynden O. Pindling. It shares its monarch with the other Commonwealth realms. The Bahamas has the fourteenth-largest gross domestic product per capita in the Americas. Its economy is based on tourism and offshore finance. Though the Bahamas is in the Lucayan Archipelago, and not on the Caribbean Sea, it is often considered part of the wider Caribbean region. The Bahamas is a full member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) but is not part of the CARICOM Single Market and Economy
Etymology: The name 'Barbados' is from either the Portuguese term os barbados or the Spanish equivalent, los barbados, both meaning 'the bearded ones'. It is unclear whether 'bearded' refers to the long, hanging roots of the bearded fig-tree (Ficus citrifolia), a species of banyan indigenous to the island, or to the allegedly bearded Kalinago (Island Caribs) who once inhabited the island, or, more fancifully, to a visual impression of a beard formed by the sea foam that sprays over the outlying coral reefs. In 1519, a map produced by the Genoese mapmaker Visconte Maggiolo showed and named Barbados in its correct position. Furthermore, the island of Barbuda in the Leewards is very similar in name and was once named 'Las Barbudas' by the Spanish.
The original name for Barbados in the Pre-Columbian era was Ichirouganaim, according to accounts by descendants of the Indigenous Arawakan-speaking tribes in other regional areas, with possible translations including 'Red land with white teeth' or 'Redstone island with teeth outside (reefs)' or simply 'Teeth'.
Colloquially, Barbadians refer to their home island as 'Bim' or other nicknames associated with Barbados, including 'Bimshire'. The origin is uncertain, but several theories exist. The National Cultural Foundation of Barbados says that 'Bim' was a word commonly used by slaves, and that it derives from the Igbo term bém from bé mụ́ meaning 'my home, kindred, kind'; the Igbo phoneme in the Igbo orthography is very close to /ɪ/. The name could have arisen due to the relatively large percentage of Igbo slaves from modern-day southeastern Nigeria arriving in Barbados in the 18th century. The words 'Bim' and 'Bimshire' are recorded in the Oxford English Dictionary and Chambers Twentieth Century Dictionaries. Another possible source for 'Bim' is reported to be in the Agricultural Reporter of 25 April 1868, where the Rev. N. Greenidge (father of one of the island's most famous scholars, Abel Hendy Jones Greenidge) suggested that Bimshire was 'introduced by an old planter listing it as a county of England'. Expressly named were 'Wiltshire, Hampshire, Berkshire and Bimshire'. Lastly, in the Daily Argosy (of Demerara, i.e. Guyana) of 1652, there is a reference to Bim as a possible corruption of 'Byam', the name of a Royalist leader against the Parliamentarians. That source suggested the followers of Byam became known as 'Bims' and that this became a word for all Barbadians.
This is a continuation of an entire series of pages that will, I hope, allow my visitors to better navigate this site. As well as displaying recipes by name, country and region of origin I am now planning a whole series of pages where recipes can be located by meal type and main ingredient. This page gives a listing of all the Indian recipes added to this site.
Barbadian/Bajan is an island country within the Lesser Antilles of the Atlantic Ocean. The capital is Bridgetown. The island is is 34 kilometres long and up to 23 km wide, covering an area of 439 km2.
Barbadian/Bajan cuisine is a mixture of African, Indian, Irish, Creole and British influences. A typical meal consists of a main dish of meat or fish, normally marinated with a mixture of herbs and spices, hot side dishes, and one or more salads.
Barbados is an island country in the Atlantic Ocean. It is part of the Lesser Antilles region of the West Indies. Despite not bordering the Caribbean Sea, it is considered to be part of the Caribbean region and is therefore the most easterly of the Caribbean islands. It lies on the boundary of the South American and Caribbean plates. Its capital and largest city is Bridgetown. It was colonized by the British and forms part of the Commonwealth.
 Location of Barbados in the Caribbean with the land mass of
Location of Barbados in the Caribbean with the land mass ofBarbados picked out and circled in red.
On 30 November 1966, Barbados moved toward political independence and assumed the status of a Commonwealth realm, becoming a separate jurisdiction with Elizabeth II as the Queen of Barbados. On 30 November 2021, Barbados transitioned to a republic within the Commonwealth, replacing its monarchy with a ceremonial president.
The country gained independence from the United Kingdom in 1973, led by Sir Lynden O. Pindling. It shares its monarch with the other Commonwealth realms. The Bahamas has the fourteenth-largest gross domestic product per capita in the Americas. Its economy is based on tourism and offshore finance. Though the Bahamas is in the Lucayan Archipelago, and not on the Caribbean Sea, it is often considered part of the wider Caribbean region. The Bahamas is a full member of the Caribbean Community (CARICOM) but is not part of the CARICOM Single Market and Economy
Etymology: The name 'Barbados' is from either the Portuguese term os barbados or the Spanish equivalent, los barbados, both meaning 'the bearded ones'. It is unclear whether 'bearded' refers to the long, hanging roots of the bearded fig-tree (Ficus citrifolia), a species of banyan indigenous to the island, or to the allegedly bearded Kalinago (Island Caribs) who once inhabited the island, or, more fancifully, to a visual impression of a beard formed by the sea foam that sprays over the outlying coral reefs. In 1519, a map produced by the Genoese mapmaker Visconte Maggiolo showed and named Barbados in its correct position. Furthermore, the island of Barbuda in the Leewards is very similar in name and was once named 'Las Barbudas' by the Spanish.
The original name for Barbados in the Pre-Columbian era was Ichirouganaim, according to accounts by descendants of the Indigenous Arawakan-speaking tribes in other regional areas, with possible translations including 'Red land with white teeth' or 'Redstone island with teeth outside (reefs)' or simply 'Teeth'.
Colloquially, Barbadians refer to their home island as 'Bim' or other nicknames associated with Barbados, including 'Bimshire'. The origin is uncertain, but several theories exist. The National Cultural Foundation of Barbados says that 'Bim' was a word commonly used by slaves, and that it derives from the Igbo term bém from bé mụ́ meaning 'my home, kindred, kind'; the Igbo phoneme in the Igbo orthography is very close to /ɪ/. The name could have arisen due to the relatively large percentage of Igbo slaves from modern-day southeastern Nigeria arriving in Barbados in the 18th century. The words 'Bim' and 'Bimshire' are recorded in the Oxford English Dictionary and Chambers Twentieth Century Dictionaries. Another possible source for 'Bim' is reported to be in the Agricultural Reporter of 25 April 1868, where the Rev. N. Greenidge (father of one of the island's most famous scholars, Abel Hendy Jones Greenidge) suggested that Bimshire was 'introduced by an old planter listing it as a county of England'. Expressly named were 'Wiltshire, Hampshire, Berkshire and Bimshire'. Lastly, in the Daily Argosy (of Demerara, i.e. Guyana) of 1652, there is a reference to Bim as a possible corruption of 'Byam', the name of a Royalist leader against the Parliamentarians. That source suggested the followers of Byam became known as 'Bims' and that this became a word for all Barbadians.
Barbadian/Bajan Cuisine:
Bajan cuisine is a mixture of African, Indian, Irish, Creole and British influences. A typical meal consists of a main dish of meat or fish, normally marinated with a mixture of herbs and spices, hot side dishes, and one or more salads. A common Bajan side dish could be pickled cucumber, fish cakes, bake, etc. The meal is usually served with one or more sauces. The national dish of Barbados is cou-cou and flying fish with spicy gravy. Another traditional meal is pudding and souse, a dish of pickled pork with spiced sweet potatoes. A wide variety of seafood and meats are also available.The alphabetical list of all the Barbadian/Bajan recipes on this site follows, (limited to 100 recipes per page). There are 19 recipes in total:
Page 1 of 1
| Bajan Aubergine Curry Origin: Barbados | Bajan Macaroni Pie Origin: Barbados | Cou-cou Origin: Barbados |
| Bajan Curry Chicken Origin: Barbados | Bajan Pepperpot Origin: Barbados | Flying Fish with Cou Cou Origin: Barbados |
| Bajan Curry Chicken 2 Origin: Barbados | Bajan Salt Bread Origin: Barbados | Pigeon Peas and Rice Origin: Barbados |
| Bajan Curry Goat Origin: Barbados | Bajan Spice Mix Origin: Barbados | Pudding and Souse Origin: Barbados |
| Bajan Curry Powder Origin: Barbados | Bajan Sunday Breakfast Origin: Barbados | Saltfish Accra Origin: Barbados |
| Bajan Curry Powder Origin: Barbados | Bajan Sweet Bread Origin: Barbados | |
| Bajan Green Seasoning Origin: Barbados | Barbadian Plain Cake Origin: Barbados |
Page 1 of 1